Setting up
Establishing a foreign business presence in Iraq is a process governed by a specific set of legal requirements and procedures. One of the most common forms for foreign companies to enter the Iraqi market is through the registration of a branch office.
This approach allows the foreign company to conduct business within Iraq while maintaining a direct connection to its headquarters abroad. Understanding the legal framework and specific obligations related to the registration and operation of a branch office in Iraq is essential for ensuring compliance and successful business operations in the region
- Branch Office – Definition
A branch office is a representative entity of the main office, where the core business activities are conducted in Iraq. This office acts on behalf of the foreign company, facilitating its operations and presence in the Iraqi market.
Most branch offices consist of smaller divisions that handle various aspects of the company’s operations, such as sales, marketing, and customer service, reflecting the broader functions of the main office.
The Iraqi law defines a branch office under Law No. 2 of 2017, Article 1, Paragraph 5: “Branch: The legal entity that represents the foreign company in Iraq.” This definition highlights the branch’s role as an extension of the foreign company, with a legal standing that enables it to engage in business activities in Iraq under the same identity as the main office.
- Distinction Between Branch and Representative Offices (RF)
RF is an old structure that is no longer used.
The primary difference between a branch office and a representative office in Iraq lies in the scope of their permitted activities:
- A representative office in Iraq is limited in its functions; it cannot enter into contracts or conduct any business transactions within Iraq. Its role is strictly confined to representing the foreign company, gathering information, and liaising with potential clients or partners.
- Under the previous regulatory framework, specifically Law No. 5 of 1989, the sole function of a representative office was to represent the foreign company in Iraq without engaging in any commercial activities.
- However, this old law was superseded by Law No. 2 of 2017, which explicitly stipulates that foreign companies are no longer permitted to open representative offices in Iraq. The new law mandates that foreign companies must establish a branch office if they wish to operate within the country.
Therefore, to legally conduct business in Iraq, foreign companies must establish a branch office rather than a representative office. The branch office is legally empowered to enter into contracts, conduct transactions, and perform other business activities on behalf of the foreign company.
Legal Framework for Registering a Branch Office in Iraq
When a foreign company decides to register a branch office in Iraq, it must adhere to several legal requirements, ensuring compliance with both Iraqi law and its home country’s regulations. The key legal requirements include:
- Home Country Registration and Compliance: The company must be properly registered and legally compliant in its home country. This includes having all necessary certifications, licenses, and adhering to the legal obligations required for operating as a business entity in its country of origin.
- Company Age Requirement: The foreign company must have been established for at least one year prior to applying for branch office registration in Iraq. This requirement ensures that only stable and established companies are permitted to enter Iraq.
- Financial Stability: The foreign company must have recorded a profit in its most recent financial year. In cases where the company has experienced a financial loss, it must demonstrate that it has sufficient capital to cover the loss amount. Alternatively, the company must have adequate assets or prove that the losses were incurred as a result of engaging in investment projects. This requirement ensures that only financially sound companies, capable of sustaining operations in Iraq, are allowed to establish a branch office.
- Company purpose: It is essential to determine the company’s activity to ensure whether it is permitted to operate in Iraq. Some companies cannot be registered in Iraq due to specific regulations that prohibit their registration, such as travel and tourism companies, law firms, and accounting audit firms.
Industry Specific Regulation
Foreign companies intending to establish a branch office in Iraq must also be aware of any industry-specific regulations that may apply to their business sector. These regulations can vary significantly depending on the nature of the business, and it is crucial for companies to understand and comply with them before proceeding with registration. Some key points to consider include:
- Sectoral Licensing Requirements: Certain industries in Iraq, such as oil and gas, telecommunications, applications, banking, Insurance and the like, are subject to specific licensing and regulatory requirements. Companies operating in these sectors may need to obtain additional approvals from relevant government ministries or regulatory bodies.
- Foreign Investment Restrictions: While Iraq generally allows foreign investment across various sectors, some industries may have restrictions on the percentage of foreign ownership or require joint ventures with local partners. It is important for foreign companies to verify these restrictions and plan accordingly.
- Government Tenders and Contracts: For companies involved in sectors where government contracts or tenders are common, it is important to understand the specific requirements and procedures for participating in such opportunities. This may include meeting pre-qualification criteria, adhering to local content requirements, and following specific procurement regulations.
- Regulations: Companies in certain industries may be required to comply with specific Iraqi standards, such as environmental regulations, safety standards, and labor laws. Ensuring compliance with these standards is critical for maintaining legal operations within Iraq.
Registration Process
Registering a branch office in Iraq involves several detailed steps that must be carefully followed to ensure compliance with Iraqi regulations. The process is designed to verify the legitimacy and readiness of the foreign company to operate in Iraq.
Document Certification: Before submitting any documents, the following certifications are required:
- Certify the documents from the notary public and other departments such as companies’ registration department or trade chamber.
- Certification by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Country of Origin): All documents must first be certified by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in the country of incorporation.
- Certification by the Iraqi Embassy (Country of Origin): The documents must then be certified by the Iraqi Embassy in the country of incorporation, ensuring that they meet Iraqi legal standards.
- Certification by the Iraqi Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Iraq): Finally, the documents must be certified by the Iraqi Ministry of Foreign Affairs to complete the certification process.

Involvement of Iraqi Authorities in the Registration Process
The registration process for a branch office in Iraq involves obtaining permission and approvals from various Iraqi authorities, each playing a critical role in ensuring the legal and regulatory compliance of the foreign company:
- Iraqi Ministry of Foreign Affairs: The Ministry is responsible for the final certification of the documents, confirming their validity and compliance with Iraqi laws.
- Iraqi Ministry of Commerce / Companies Registration Department: This department is the primary authority overseeing the registration process, including the review of applications and issuance of the branch registration license.
- Iraqi Bar Association: In certain cases, particularly for companies providing legal or advisory services, permission must be obtained from the Iraqi Bar Association, ensuring that the company meets professional standards.
- Local Government Authorities: The local government where the branch office is located must confirm the business premises and ensure compliance with local zoning and business regulations.
Required Documents for Branch Office Registration
The following documents are required to successfully register a branch office in Iraq:
- Articles of Association or Equivalent. Document: This document outlines the structure and regulations governing the foreign company.
- Certificate of Incorporation or Equivalent Document: Proof of the company’s legal existence in its home country.
- Final Accounts: Financial statements for the last financial year or the preceding financial year, demonstrating the company’s financial stability.
- List of Board Members and Authorized Signatories: Prepared by the lawyer, Names of the board members or managing director, individuals authorized to sign on behalf of the company, and all shareholders.
- Document Appointing the Branch
Manager: Prepared by the lawyer, a formal document designating the individual responsible for managing the branch office in Iraq.
- Pledge Document: Prepared by the lawyer, as instructed by the Companies Registration Department, this document is a formal commitment to adhere to Iraqi laws and regulations.
- Beneficial Ownership Information: Prepared by the lawyer, as instructed by CBI Details on the beneficial owners of the company, ensuring transparency in ownership.
- List of Additional Information: Prepared by the lawyer, Any other documents or information requested by the registrar during the registration process.
- Passport of branch manager.
Step-by-Step Process for Registering a Foreign Branch Office in Iraq
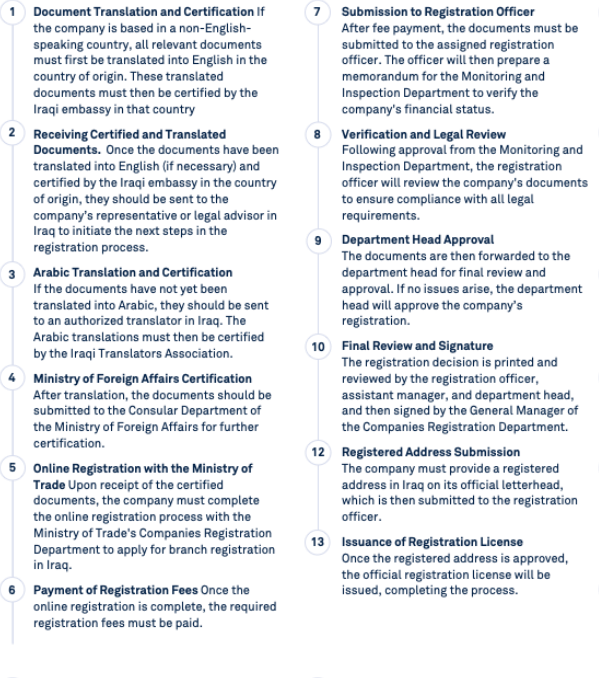
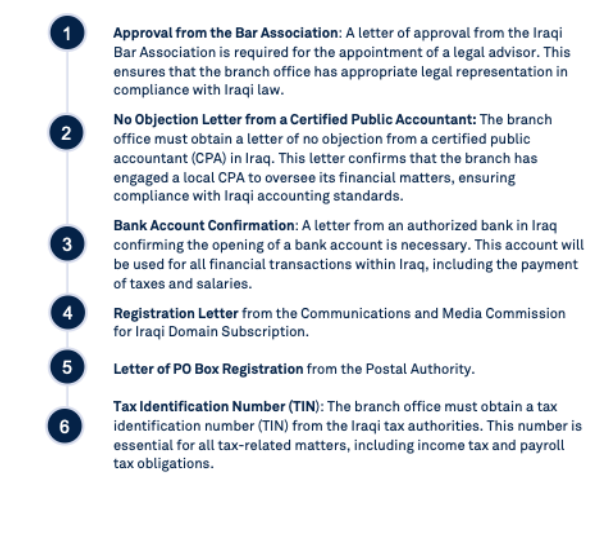
Steps to Commence Operations After Registration
Once a foreign branch office is successfully registered in Iraq, there are several critical steps that must be taken to commence operations:
Tax Obligation Foreign Branch Office in Iraq
Foreign branch offices operating in Iraq are subject to several tax obligations, which must be fulfilled to remain compliant with local laws.
Income Tax: The branch office is required to pay income tax on its profits at the end of each financial year. The tax rate and payment schedule are governed by Iraqi tax laws, and timely payment is essential to avoid penalties. The Income Tax Rate up to 15%.
Payroll Tax: Payroll tax is imposed on the salaries of the branch manager and all employees working at the branch office. This tax must be calculated and paid regularly, ensuring compliance with Iraqi labor and tax regulations. This is 15% for Iraqi (this will very depending on the circumstances of the Individual) and up to 25% including social Security for an Expat.
Mandatory Local Hires and Management Positions: In accordance with Iraqi labor laws, foreign branch offices must adhere to specific requirements regarding the employment of Iraqi nationals.
Local Hiring Requirement: For every foreign worker employed by the branch office, approximately two Iraqi citizens must be hired. This regulation is intended to promote local employment and ensure that foreign companies contribute to the Iraqi labor market.
Ministry of Labor Approval for Workforce Composition: In certain cases, it is possible to obtain approval from the Iraqi Ministry of Labor to hire a workforce consisting of 50% Iraqi nationals and 50% foreign workers. This approval is typically granted when specific skills or expertise are not readily available within the local workforce.
Ongoing Compliance Requirements: Foreign branch offices in Iraq must fulfill ongoing compliance requirements to maintain their legal status and continue operations:
Annual Financial Statements: The branch office must submit its financial statements for the completed fiscal year to the relevant Iraqi authorities by August 30th of each year.
Annual Confirmation of Business Location: The branch office must provide an annual confirmation of its business location, verified by the local government, to ensure that the office is operating within a legally recognized premises.
Renewal of Legal Advisor’s Letter: The letter of approval from the legal advisor must be renewed every six months, ensuring that the branch office continues to have valid legal representation.
Social Security Contributions: Social security contributions for employees must be paid at the beginning of each month, in accordance with Iraqi labor laws.
Contribution Breakdown: The total contribution amounts to 17% of the employee’s salary, with 12% paid by the employee and 5% paid by the employer.
Salary Cap: The contribution is capped at a salary of 1,750,000 IQD, meaning the percentage applies only up to this salary limit.
Ongoing Compliance Requirements
Foreign branch offices in Iraq must fulfill ongoing compliance requirements to maintain their legal status and continue operations:
Annual Financial Statements: The branch office must submit its financial statements for the completed fiscal year to the relevant Iraqi authorities by August 30th of each year.
Annual Confirmation of Business Location: The branch office must provide an annual confirmation of its business location, verified by the local government, to ensure that the office is operating within a legally recognized premises.
Renewal of Legal Rep at the Bar : The letter of approval from the legal advisor must be renewed every six months, ensuring that the branch office continues to have valid legal representation.
Social Security Contributions: Social security contributions for employees must be paid at the beginning of each month, in accordance with Iraqi labor laws.
Domain name and PO Box: Annual Renewal is required.
Challenges & Considerations
Foreign companies may encounter several challenges during the process of registering and operating a branch office in Iraq. These are outlined below:
- Timely Submission of Financial Statements Annually: The company must submit its financial statements for the completed fiscal year by August 30th annually. Failure to meet this deadline can result in penalties and legal complications.
- Annual Location Confirmation: The branch office must provide annual confirmation of its business location from the local government. Ensuring timely compliance with this requirement is essential for maintaining the branch’s legal status.
- Legal Advisor’s Letter Renewal: The legal advisor’s approval letter must be renewed every six months, which requires consistent attention to avoid penalties by the Iraqi bar.
- Social Security Payments: Monthly social security contributions must be paid promptly to avoid penalties.




